
In the case of single-field formats, such as UTM, the original UTM field is maintained, and two fields are added, appended with _X and _Y and display the coordinate information in decimal degrees. For example, if the coordinate information is stored in a text field in degrees, minutes, and seconds (for example, -120 13 58), it is converted and displayed in decimal degrees. Sometimes the information you need is stored in a different format or naming convention. In the example above, the coordinate information was straightforward and easy to recognize, contained in fields x and y. If a delimited text file contains data coordinate information, such as x,y data, ArcGIS Pro recognizes the coordinate information as numeric fields that can be used to display your information either as a layer or as input to tasks, such as geocoding. The following is an example of a comma-delimited text file:Ĩ.01,44.3,003,orange How coordinate information is determined Use commas or tabs to delineate the columns. The first row of a text file can contain the column headings, and the subsequent rows can contain coordinates and attributes.

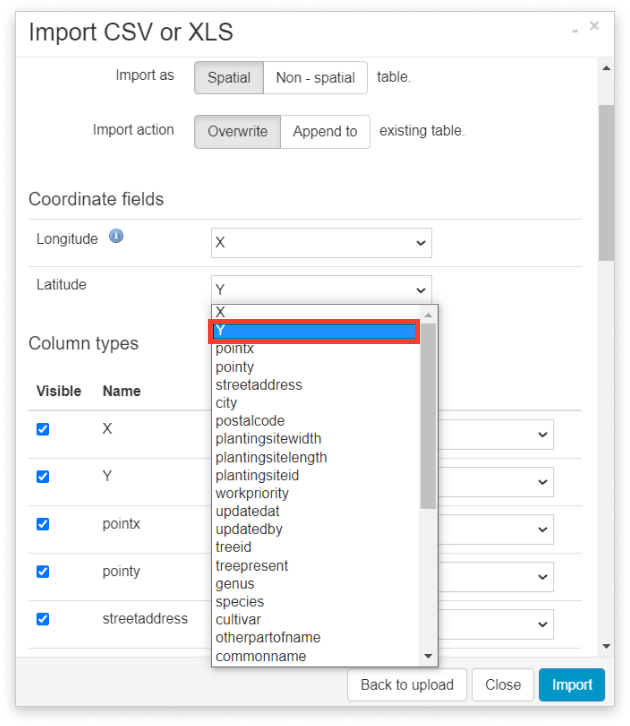
tab extension to differentiate text files with delimited data from unformatted text files. To avoid the error, ensure that delimited text files have a. If you try to display a text file that doesn't contain tabular data, the data is displayed as a table if possible, or an error occurs. Any file with one of these extensions is interpreted as a text file table even if it doesn't contain tabular data. tab extension are interpreted as tab delimited by default. csv extension are interpreted as comma delimited, while files with a. tab extensions and assign them a file type of text file.įiles with a. The Catalog pane and the Add Data dialog box list files with. In ArcGIS Pro, you can access data in delimited text files and work with them as tables.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
